3 000 Mcg To Iu
wordexpert
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
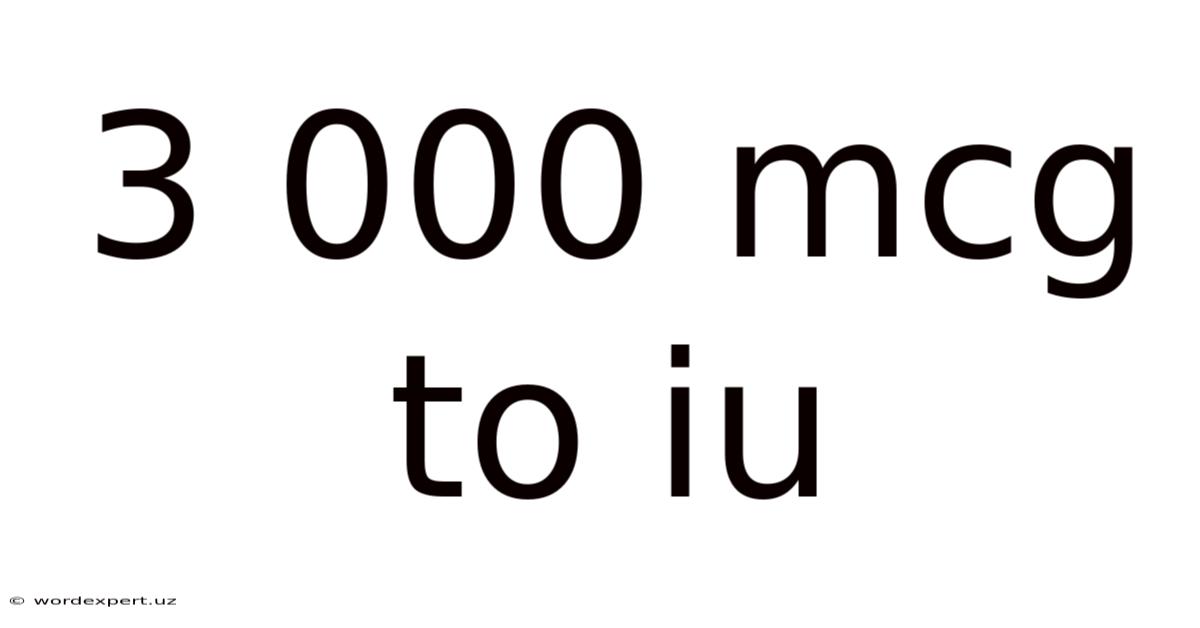
Table of Contents
Decoding the Conversion: 3000 mcg to IU – A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding vitamin and supplement dosages can be confusing, especially when dealing with different units of measurement. This article will thoroughly explain the conversion of micrograms (mcg) to International Units (IU), focusing specifically on the conversion of 3000 mcg to IU. We'll explore the nuances of this conversion, explain the scientific basis behind it, address common FAQs, and provide a clear understanding of how to apply this knowledge in your daily life. This guide will empower you to confidently navigate supplement labels and make informed decisions about your health.
Understanding mcg and IU
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify what mcg and IU represent.
-
Micrograms (mcg): This is a unit of mass in the metric system. One microgram is one millionth of a gram (1 mcg = 0.000001 g). It's commonly used to measure the mass of vitamins and minerals, such as Vitamin D, Vitamin B12, and many others.
-
International Units (IU): This is a unit of biological activity. It's not a standard unit of mass or weight but rather a measure of the effect a substance has. The IU value for a specific vitamin or nutrient varies depending on its biological activity. This means that the conversion from mcg to IU isn't a simple mathematical equation; it's dependent on the specific vitamin or nutrient in question. For example, 1 mcg of Vitamin D3 doesn't equal 1 IU of Vitamin D3; the conversion factor differs.
The crucial point is: You cannot directly convert 3000 mcg to IU without knowing which vitamin or nutrient those 3000 mcg refer to.
The Challenge of Direct Conversion: Why it's Not Always Simple
The lack of a universal conversion factor between mcg and IU stems from the varying biological activity of different substances. International Units are defined based on a biological standard – the effect a specific amount of the substance has on a biological system. This standard is often established through bioassays and can change slightly over time as measurement techniques improve.
For instance, the conversion factor for Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) differs from that of Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol), even though both are forms of Vitamin D. The IU value reflects the vitamin's capacity to raise blood calcium levels, and this capacity can slightly vary between the two forms.
Case Study: Vitamin D Conversion
Let's illustrate the conversion process using Vitamin D as an example. This is a commonly encountered scenario, as Vitamin D is often measured in both mcg and IU.
Generally, 1 mcg of Vitamin D3 is equivalent to approximately 40 IU. Therefore, to convert 3000 mcg of Vitamin D3 to IU, we use the following calculation:
3000 mcg * 40 IU/mcg = 120,000 IU
However, it's crucial to note that this is an approximation. Different manufacturers and regulatory bodies might use slightly varying conversion factors. Always check the specific information provided by the supplement manufacturer. The label should explicitly state the conversion if it offers the supplement in both mcg and IU.
Other Vitamins and Nutrients: The Need for Specific Information
For vitamins and nutrients other than Vitamin D, the conversion factor from mcg to IU will differ significantly. There isn't a single, universally applicable conversion chart.
-
Vitamin A: The conversion depends on whether you are considering retinol (Vitamin A) or beta-carotene (a precursor to Vitamin A). Retinol is directly usable by the body and has a different IU equivalent than beta-carotene.
-
Vitamin E: Vitamin E also has several forms, each with a different IU equivalent. Alpha-tocopherol is the most biologically active form.
-
Other Nutrients: Many other nutrients are measured in mcg (e.g., various B vitamins, minerals like selenium) but are not expressed in IU. The IU system is primarily used for fat-soluble vitamins where a direct mass-to-activity relationship isn't readily established.
Therefore, if you have a 3000 mcg quantity of a vitamin or nutrient other than Vitamin D3, you must consult the product label or a reliable scientific source for the correct mcg to IU conversion factor.
Practical Implications and Considerations
The accurate conversion between mcg and IU is crucial for ensuring you receive the correct dosage of vitamins and supplements. An incorrect conversion can lead to either deficiency or toxicity.
-
Always check the supplement label: The manufacturer should clearly state the amount of the nutrient in both mcg and IU (if applicable) to avoid any confusion.
-
Consult a healthcare professional: If you have questions about the appropriate dosage of a particular vitamin or nutrient, consult with a doctor, registered dietitian, or other qualified healthcare provider. They can help you determine the best dosage based on your individual needs and health status.
-
Be aware of variations: Remember that slight variations in conversion factors may exist depending on the source and manufacturing process.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is it safe to take 120,000 IU of Vitamin D daily?
A1: No, a daily intake of 120,000 IU of Vitamin D is generally considered excessively high and could potentially lead to hypervitaminosis D (Vitamin D toxicity), characterized by high blood calcium levels which can cause various health problems. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for Vitamin D varies depending on individual factors such as age, health status, and sun exposure. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for your individual needs.
Q2: Why are some vitamins measured in IU while others are measured in mcg?
A2: International Units are primarily used for fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) because their biological activity is not directly proportional to their weight. Water-soluble vitamins (such as B vitamins and C) are generally measured in mcg (or mg) as their biological activity is more directly related to their weight.
Q3: Where can I find reliable conversion factors for vitamins other than Vitamin D?
A3: Reliable sources for conversion factors include scientific literature, reputable health organizations (e.g., the National Institutes of Health), and the product labels themselves. Always prioritize information from peer-reviewed scientific publications and trusted health professionals.
Q4: Can I convert mcg to IU for all supplements?
A4: No, not all supplements use the IU system. Many minerals and water-soluble vitamins are measured solely in mcg, mg, or other units of mass.
Conclusion: The Importance of Precision in Supplementation
Understanding the nuances of mcg and IU conversion is crucial for safe and effective supplementation. While a simple calculation can often be used for Vitamin D3, remember that this is an approximation and that the conversion factor varies depending on the specific vitamin or nutrient. Always prioritize consulting product labels and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and health goals. Taking the necessary precautions ensures your supplementation journey is both effective and safe. Avoid self-diagnosing and self-medicating; always rely on professional guidance when making decisions about your health and wellness.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
500 Square Meter In Feet
Sep 13, 2025
-
Ft Cubed To Inches Cubed
Sep 13, 2025
-
650 Nm To Ft Lbs
Sep 13, 2025
-
How To Calculate Double Time
Sep 13, 2025
-
Traductor De Pies A Cm
Sep 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 000 Mcg To Iu . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.