40 Trillion / 80 Million
wordexpert
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
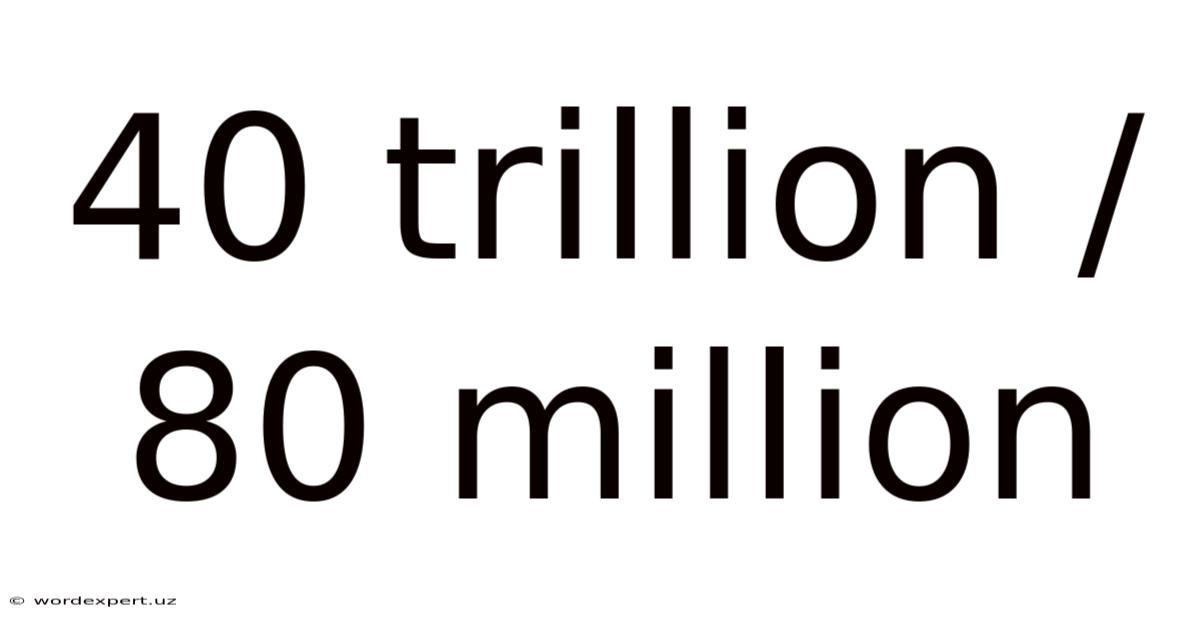
Table of Contents
Decoding the Immense: Understanding 40 Trillion Divided by 80 Million
This article explores the seemingly daunting calculation of 40 trillion divided by 80 million, breaking down the process step-by-step and delving into its real-world implications. We'll uncover the underlying mathematical principles, examine practical applications of this type of calculation, and address frequently asked questions to provide a comprehensive understanding of this significant numerical operation. Understanding large-scale divisions like this is crucial in various fields, from finance and economics to scientific research and data analysis.
Understanding the Basics: Large Number Division
Before diving into the specifics of 40 trillion divided by 80 million, let's refresh our understanding of division with large numbers. Dividing a large number by a smaller number essentially means finding out how many times the smaller number fits into the larger number. In this case, we want to determine how many times 80 million goes into 40 trillion.
This type of problem might seem intimidating at first glance due to the sheer size of the numbers involved. However, by employing a systematic approach and understanding scientific notation, we can simplify the process considerably.
Simplifying the Calculation: Scientific Notation
Scientific notation is a powerful tool for working with extremely large or small numbers. It expresses numbers in the form of a a x 10<sup>b</sup>, where 'a' is a number between 1 and 10, and 'b' is an integer exponent representing the power of 10.
Let's convert 40 trillion and 80 million into scientific notation:
- 40 trillion: 40,000,000,000,000 = 4 x 10<sup>13</sup>
- 80 million: 80,000,000 = 8 x 10<sup>7</sup>
Now, our division problem becomes: (4 x 10<sup>13</sup>) / (8 x 10<sup>7</sup>)
Performing the Division
We can simplify this expression by dividing the coefficients (4 and 8) and subtracting the exponents of 10:
(4 / 8) x 10<sup>(13 - 7)</sup> = 0.5 x 10<sup>6</sup>
To express the result in standard scientific notation, we need to adjust the coefficient to be between 1 and 10. We can do this by moving the decimal point one place to the right and decreasing the exponent by 1:
0.5 x 10<sup>6</sup> = 5 x 10<sup>5</sup>
The Answer and its Significance: 500,000
Therefore, 40 trillion divided by 80 million equals 500,000. This result highlights the immense scale involved. It demonstrates how a seemingly small number (80 million) can be contained within a vastly larger one (40 trillion) a significant number of times.
This simple calculation has far-reaching implications depending on the context. For instance, if we were analyzing a national budget where 40 trillion represented the total expenditure and 80 million represented the population, then 500,000 would represent the per capita expenditure.
Real-World Applications: Exploring the Context
The application of this type of calculation is vast. Let's explore some examples:
- National Budgets and Per Capita Income: As mentioned earlier, dividing a nation's total budget by its population provides the per capita expenditure. This metric is crucial for understanding the financial well-being of a country's citizens.
- Resource Allocation: Imagine a company with 40 trillion units of a resource needing to distribute it evenly among 80 million customers. The result (500,000) represents the amount each customer would receive.
- Scientific Research: In scientific fields like astronomy or particle physics, dealing with massive datasets is commonplace. Dividing large datasets by smaller sample sizes is fundamental for statistical analysis.
- Economic Indicators: In economics, analyzing gross domestic product (GDP) against population figures will reveal per capita GDP, another crucial economic indicator.
- Environmental Studies: Calculating the distribution of pollutants or resources across a large geographical area often involves such calculations.
Expanding the Understanding: Beyond the Calculation
While the numerical answer is important, it's crucial to understand the context behind the numbers. The values of 40 trillion and 80 million are likely representing specific quantities in a real-world situation.
For example:
- 40 trillion could represent: The national debt of a country, the total market capitalization of a stock exchange, the total number of grains of sand on a beach (a highly speculative number, but used to illustrate the scale).
- 80 million could represent: The population of a large country, the number of active users of a social media platform, the number of vehicles on a continent's roads.
The significance of the result (500,000) will always be dependent on the context and the units of measurement involved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can this calculation be done using a calculator?
A: Absolutely. Most standard calculators can handle this calculation directly. However, understanding the underlying principles and the use of scientific notation remains essential for comprehending the magnitude of the result.
Q: What if the numbers were different? How would the process change?
A: The process remains the same. Convert the numbers into scientific notation, divide the coefficients, and subtract the exponents. The complexity might vary based on the numbers themselves.
Q: Are there any potential errors in the calculation?
A: The potential for error primarily lies in the accuracy of the initial input values. If the numbers 40 trillion and 80 million are estimations rather than precise figures, then the final result will also be an estimation.
Q: What are some alternative methods to solve this problem?
A: While scientific notation provides an efficient approach, long division could be used, though it would be considerably more time-consuming with such large numbers. Spreadsheet software can also perform this calculation.
Q: Why is understanding this type of calculation important?
A: Understanding calculations involving very large numbers is crucial in various fields for making informed decisions, interpreting data, and gaining insights into complex systems. It's essential for analyzing financial data, understanding population dynamics, and interpreting scientific findings.
Conclusion: Mastering Large-Scale Division
The division of 40 trillion by 80 million, resulting in 500,000, might seem like a simple mathematical operation. However, its significance extends beyond the numerical answer. Understanding the process, the underlying principles, and the context in which such calculations are applied provides a powerful tool for analyzing complex data and making informed decisions in various fields. Mastering this type of calculation empowers us to grapple with the vast scales encountered in the real world, translating raw data into meaningful insights. From national budgets to scientific discoveries, the ability to handle large-scale division is a valuable asset in numerous fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long Until 1 20
Sep 23, 2025
-
How Long Is 105 Weeks
Sep 23, 2025
-
How Many Days Is 10080
Sep 23, 2025
-
Conversor De Onzas A Litros
Sep 23, 2025
-
60 Days From July 10
Sep 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 40 Trillion / 80 Million . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.