What Is 1 Of 100000
wordexpert
Sep 13, 2025 · 6 min read
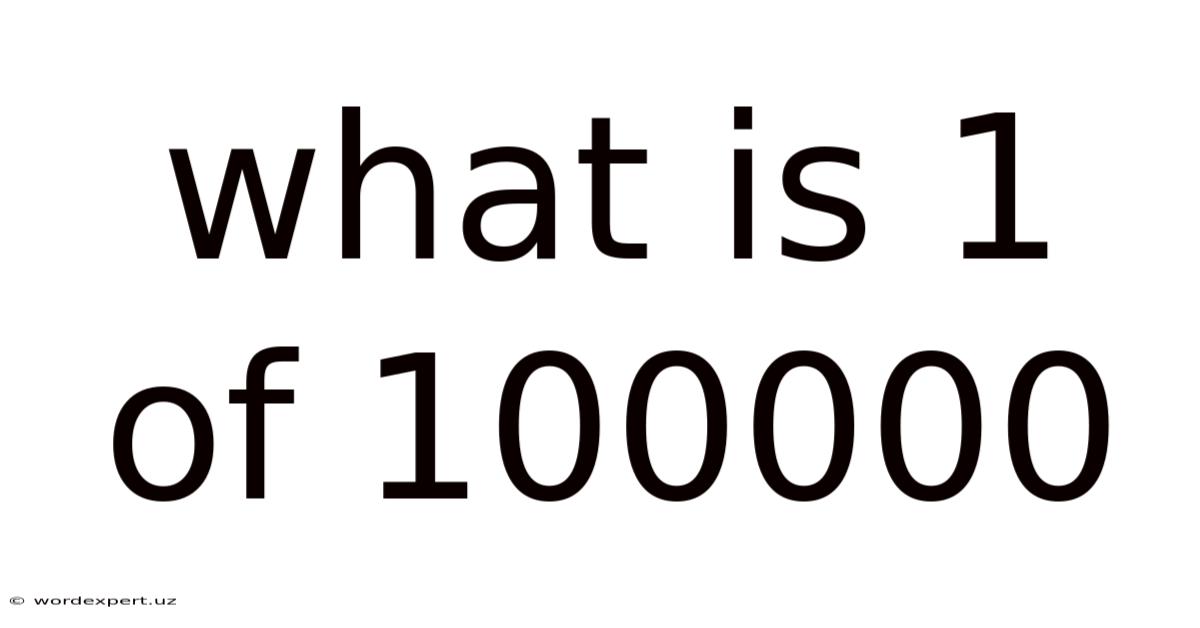
Table of Contents
What is 1 out of 100,000? Understanding Probability and Rare Events
Understanding the concept of "1 out of 100,000" requires delving into the world of probability and statistics. It represents an incredibly small probability, a rare event with a low likelihood of occurrence. This seemingly simple phrase carries significant implications across various fields, from risk assessment and medical diagnosis to lottery odds and scientific research. This article will explore this concept in detail, explaining its meaning, its practical applications, and how to grasp its significance within different contexts.
What Does 1 in 100,000 Mean?
At its core, "1 out of 100,000" expresses a probability or chance. It signifies that for every 100,000 instances or trials, one specific event is expected to occur. This can be expressed as a fraction (1/100,000), a decimal (0.00001), or a percentage (0.001%). The key takeaway is the extreme rarity of the event. It's highly unlikely to happen in any given trial, but the possibility remains.
Understanding Probability and its Implications
Probability measures the likelihood of an event occurring. It ranges from 0 (impossible) to 1 (certain). An event with a probability of 1/100,000 lies extremely close to 0, indicating a very low chance of happening. However, it's crucial to remember that even with a low probability, the event could still occur. This is where the concept of randomness and chance play a critical role.
The low probability of 1 in 100,000 doesn't mean the event is impossible; it merely states that it's highly improbable. This distinction is important, especially when dealing with:
-
Risk Assessment: In fields like safety engineering or public health, understanding such low probabilities is vital for evaluating risks. While a 1 in 100,000 chance of a catastrophic event might seem negligible, the potential consequences could be severe enough to warrant preventative measures.
-
Medical Diagnosis: A certain disease might have a prevalence of 1 in 100,000 in the general population. This means that a positive diagnostic test result, even with high accuracy, needs careful interpretation, considering the low base rate of the disease. False positives become a significant concern in such cases.
-
Scientific Research: In scientific experiments, low probabilities can be crucial in determining the statistical significance of findings. A result that occurs with a probability as low as 1 in 100,000 might be considered statistically significant, providing strong evidence supporting a hypothesis.
-
Lottery Odds: Lottery games often involve astronomically low probabilities of winning. Understanding the odds—which might be expressed as 1 in millions or even billions—helps individuals make informed decisions about participation.
Visualizing 1 in 100,000
To better grasp the magnitude of 1 in 100,000, consider these analogies:
-
A Large City's Population: Imagine a city with a population of 100,000 people. The probability of randomly selecting a specific individual from that city is 1 in 100,000.
-
A Stadium Crowd: Visualize a large stadium filled with 100,000 spectators. The probability of randomly picking a single person from the crowd is 1 in 100,000.
-
Coin Tosses: While unlikely, the probability of getting 17 consecutive heads in a fair coin toss sequence is similar to 1 in 100,000.
These analogies help to illustrate the sheer rarity of an event with a probability of 1 in 100,000.
Calculating Probabilities: From Fractions to Percentages
To work with probabilities, understanding different representations is crucial:
-
Fraction: 1/100,000 directly shows the ratio of favorable outcomes to total possible outcomes.
-
Decimal: 0.00001 is the decimal equivalent of the fraction, obtained by dividing 1 by 100,000.
-
Percentage: 0.001% represents the probability as a percentage, obtained by multiplying the decimal by 100.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
Let’s explore how the concept of "1 in 100,000" applies in real-world scenarios:
1. Rare Diseases: Many genetic disorders or rare diseases affect only a small fraction of the population. A disease with a prevalence of 1 in 100,000 means that only one person out of every 100,000 is expected to have the disease. This low prevalence has significant implications for research funding, drug development, and patient care.
2. Adverse Drug Reactions: Some medications can cause rare but serious side effects. The probability of experiencing a specific adverse reaction might be stated as 1 in 100,000. This information is crucial for informing patients about potential risks and benefits.
3. Industrial Safety: In manufacturing processes, the probability of a specific equipment malfunction causing an accident might be 1 in 100,000. Risk assessments involve calculating such probabilities to implement safety measures and reduce potential hazards.
4. Aviation Safety: The aviation industry has extremely high safety standards. The probability of a fatal accident for a particular aircraft type might be expressed in terms like 1 in 100,000 flight hours. This low probability is a result of stringent safety regulations and meticulous maintenance protocols.
5. Natural Disasters: Certain natural events, like extremely powerful hurricanes hitting a specific location, may have probabilities in the range of 1 in 100,000 in a given year. Understanding such probabilities helps in disaster preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is an event with a probability of 1 in 100,000 impossible?
A: No, it's highly improbable but not impossible. While extremely unlikely, the event could still occur due to random chance.
Q: How can I calculate the probability of an event not happening if the probability of it happening is 1 in 100,000?
A: The probability of the event not happening is 99,999/100,000 or approximately 0.99999 (99.999%).
Q: Can I use this probability to predict the future?
A: No, probability only provides a measure of likelihood, not a guarantee. It doesn't allow for precise prediction of when or if the event will occur. It's a tool for understanding risk and chance.
Q: How does sample size affect the observed probability?
A: With smaller samples, the observed probability might deviate significantly from the theoretical probability of 1 in 100,000. Larger sample sizes provide a more accurate representation of the true probability.
Conclusion: Embracing Uncertainty and Low Probabilities
The concept of "1 out of 100,000" highlights the importance of understanding probability in various contexts. While representing an incredibly low likelihood, it's crucial to remember that such events are not impossible. Understanding these low probabilities allows for better risk assessment, informed decision-making, and a more realistic understanding of the world's inherent uncertainties. Whether dealing with rare diseases, industrial accidents, or lottery odds, grasping the significance of such low probabilities equips individuals with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of chance and make informed choices. It's a reminder that while some events are highly improbable, they are not entirely outside the realm of possibility.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Uncooked To Cooked Rice Calculator
Sep 13, 2025
-
Conversion De Gramos A Onzas
Sep 13, 2025
-
What Is 8 Of 10
Sep 13, 2025
-
13 Mil Pasos A Km
Sep 13, 2025
-
Meters To Meters Squared Converter
Sep 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 1 Of 100000 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.