50 000 Kb To Mb
wordexpert
Sep 22, 2025 · 6 min read
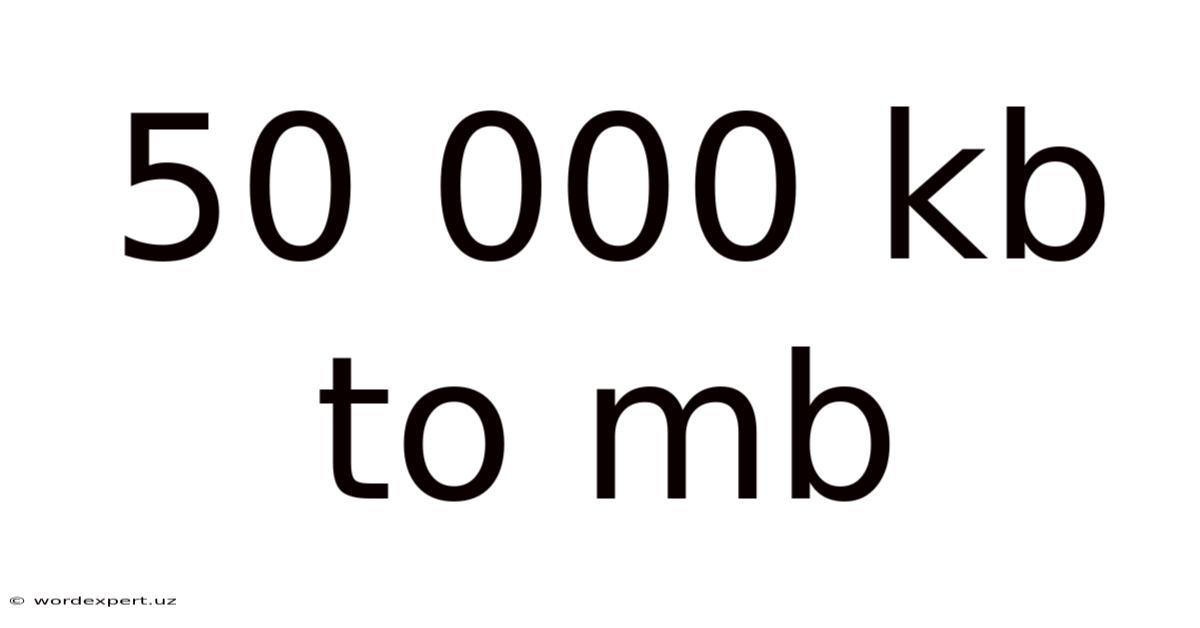
Table of Contents
Converting 50,000 KB to MB: A Comprehensive Guide to Data Measurement
Understanding data storage and the relationship between different units of measurement, like kilobytes (KB) and megabytes (MB), is crucial in today's digital world. This comprehensive guide will not only show you how to convert 50,000 KB to MB but also delve into the underlying principles, providing you with a solid understanding of data measurement and its practical applications. Whether you're a student grappling with computer science concepts, a professional managing digital assets, or simply a curious individual, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the world of digital data. We'll explore the conversion process, delve into the history of these units, and address frequently asked questions to ensure a complete understanding.
Understanding Kilobytes (KB) and Megabytes (MB)
Before we dive into the conversion, let's clarify what kilobytes and megabytes represent. These are units used to measure digital information, essentially representing the amount of data a computer can store or process. They are part of a larger system of units based on powers of two, reflecting the binary nature of computers.
-
Kilobyte (KB): A kilobyte is equal to 1024 bytes (2<sup>10</sup> bytes). A byte is the basic unit of digital information, typically representing a single character or a small piece of data. Think of a kilobyte as a small amount of data; a short text message or a small image file might be measured in kilobytes.
-
Megabyte (MB): A megabyte is equal to 1024 kilobytes (2<sup>20</sup> bytes). It's a larger unit, representing a significantly greater amount of data. A typical song file, a short video clip, or several hundred pages of text could be measured in megabytes.
The relationship between KB and MB is fundamental: 1 MB = 1024 KB. This is a key piece of information needed for our conversion. The use of 1024 (a power of two) instead of 1000 (a power of ten) stems from the binary system used in computers. While sometimes 1000 is used (especially in decimal approximations), sticking to the proper binary definition is crucial for accurate data representation.
Calculating 50,000 KB to MB
Now that we understand the relationship between KB and MB, let's perform the conversion. To convert 50,000 KB to MB, we simply divide the number of kilobytes by 1024:
50,000 KB / 1024 KB/MB ≈ 48.83 MB
Therefore, 50,000 KB is approximately equal to 48.83 MB.
It’s important to note that this is an approximation. Because we are using 1024 as a divisor, the result may not be a whole number, leading to a decimal value. The use of decimal places ensures more accurate representation of the data size.
A Deeper Dive into Data Measurement Units
The kilobyte and megabyte are just two units in a larger hierarchy of data measurement. Understanding this hierarchy provides a broader perspective on data scales. The common units include:
- Bit (b): The smallest unit of data, representing a single binary digit (0 or 1).
- Byte (B): 8 bits.
- Kilobyte (KB): 1024 bytes (approximately 1,000 bytes)
- Megabyte (MB): 1024 kilobytes (approximately 1,000,000 bytes)
- Gigabyte (GB): 1024 megabytes (approximately 1,000,000,000 bytes)
- Terabyte (TB): 1024 gigabytes (approximately 1,000,000,000,000 bytes)
- Petabyte (PB): 1024 terabytes (approximately 1,000,000,000,000,000 bytes)
- Exabyte (EB): 1024 petabytes
- Zettabyte (ZB): 1024 exabytes
- Yottabyte (YB): 1024 zettabytes
This list illustrates the exponential growth in data storage capacity. Understanding this scale is essential for comprehending the vast amounts of data generated and stored daily.
Practical Applications of Data Conversions
Converting between different units of data measurement has several practical applications:
-
File Management: Knowing the size of files helps in managing storage space on computers, hard drives, and cloud storage services. Converting KB to MB (or other units) gives a clearer picture of how much space a file or group of files occupies.
-
Network Bandwidth: Understanding data sizes is crucial for calculating download and upload speeds. Network bandwidth is often measured in MBps (megabytes per second) or GBps (gigabytes per second). Knowing file sizes helps estimate download times.
-
Data Analysis: In data science and related fields, converting between units is essential for data interpretation and analysis. Large datasets are often measured in terabytes or even petabytes.
-
Software Development: Software developers need to be mindful of data sizes when designing and implementing applications. Efficient data handling is crucial for optimal performance.
-
Digital Media: When working with images, videos, and audio files, understanding file sizes allows for more efficient storage and sharing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is 1 KB equal to 1024 bytes, not 1000 bytes?
A: This stems from the binary nature of computers. Computers work with binary code (0s and 1s), and powers of two are more naturally aligned with this system. While 1000 is a convenient approximation, 1024 (2<sup>10</sup>) is the precise representation.
Q: Are there any online converters for KB to MB?
A: While many online converters exist, performing the calculation manually strengthens understanding. However, if you need a quick conversion for numerous values, using an online tool can be efficient.
Q: What about other data units like GB or TB? How do I convert them?
A: The principle remains the same. You would use the following conversions:
- KB to GB: Divide by 1024 twice (or divide by 1,048,576).
- MB to GB: Divide by 1024.
- GB to TB: Divide by 1024.
And so on, following the power-of-two relationship between the units.
Q: What happens if I try to store a file larger than my available storage space?
A: You will encounter an error. The operating system will usually prevent the file from being saved until sufficient free space is available.
Q: Does the type of file affect its size?
A: Yes, the file type significantly influences its size. A compressed file (like a .zip file) will generally be smaller than its uncompressed counterpart. Different file formats also have varying degrees of efficiency in data storage. For instance, a high-resolution image will generally occupy more space than a low-resolution one.
Conclusion
Converting 50,000 KB to MB, while seemingly a simple task, opens a window into a world of data measurement and management. Understanding the relationship between kilobytes, megabytes, and other units is crucial for navigating the digital landscape effectively. This guide not only provides the answer to the initial conversion but also fosters a deeper understanding of data sizes and their implications in various contexts, equipping you with practical skills and knowledge for the digital age. Remember, mastering these basic concepts lays the foundation for understanding more advanced topics in computer science, data analysis, and digital technology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Bikini For Your Body Shape
Sep 22, 2025
-
Formula For Calculating Moisture Content
Sep 22, 2025
-
How Man Mg In Ml
Sep 22, 2025
-
Cuantos Cm Es Un Pie
Sep 22, 2025
-
170 000 Km In Miles
Sep 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 50 000 Kb To Mb . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.